Applying Google Analytics to your entire site with a single IIS rewrite rule
WEBBY STUFF , Windows 2008 Server No Comments »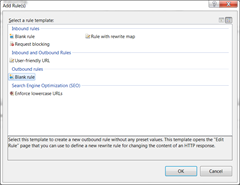 Google analytics is brilliant, of that there is no doubt, and it has replaced website stats for many people these days, however applying it to your entire site can be a pain if you have a large site and do not have a modern CMS system that allows you to easily insert scripts onto every page.
Google analytics is brilliant, of that there is no doubt, and it has replaced website stats for many people these days, however applying it to your entire site can be a pain if you have a large site and do not have a modern CMS system that allows you to easily insert scripts onto every page.
This can create a dilemma if you want to do away with website stats entirely and encourage customers to use Google analytics instead, but many customers have old legacy sites and do not have the required skills (or inclination) to do the required work, so I started looking for a way that Google analytics could be easily and automatically added to a customers site without making code changes.
Being a windows/IIS guy I first looked into using the URL rewrite engine, which allows you to create OUTGOING rules to rewrite content before it is delivered to the client, and it turned out this did the job nicely, although with the caveat that you cannot just insert raw JavaScript as some characters break the URL rewriting engine, so you have to do a bit of manipulation to get things working.
Basically you have to remove all newline characters and encode any {curly braces} as these have special meaning in url rewriting.
I actually solved this back in 2012, but it has sat unused until now as I still needed an easy way for non technical customers to do this and apply it to their websites. Well today I was having my first play with JSFiddle.net (as some have suggested I do something similar for cflive.net) and decided to do something constructive and throw together a quick script to generate the required rewrite rule to do the above, and here it is.
It is very small and very simple, but I hope useful script that will convert your analytics code into the required format and also generate the rewrite rule for you to insert into your web.config file. Just click the Result tab below to actually use the script.



Recent Comments