email authentication
& Managed Dmarc
Protect your domain from cybercriminals and spammers
We implement email authentication using SPF, DKIM and monitoring with DMARC to prevent cybercriminals from sending fraudulent and spam emails from your domain and to improve email deliverability and stop your emails going to spam.
Starting February 2024, email Authentication is now a requirement
Google and Yahoo are turning what was once considered best practices for email authentication into mandatory requirements. Senders who don’t comply with the new requirements will start to see issues getting their emails delivered as of Feb 2024. If you want to make sure your emails get delivered to your recipient’s inbox, you must get your email authentication in place.
This includes messages sent on behalf of your organization by any third-party system or email service providers (ESPs), such as CRM’s, newsletters, billing systems, etc.

Keep your domain off blacklists & protect your reputation
Stop Hackers, spammers & cybercriminals Sending Emails From Your Domain

Solve email deliverability issues, stop your emails going to spam/junk folder

- Prevent Data Leakage
- Protect Against Financial Loss
- Prevent Customer Loss
- Secure Your Email Accounts
- Protect against spoofing and spamming
- Protect your reputation
- Keep your domain off blacklists
What is email authentication?
Email authentication is a technical solution to proving that an email is not forged. In other words, it provides a way to verify that an email comes from who it claims to be from. Email authentication is most often used to block harmful or fraudulent uses of email such as phishing and spam.
In practice, we use the term “email authentication” to refer to technical standards that make this verification possible. The most commonly used email authentication standards are SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. These standards were designed to supplement SMTP, the basic protocol used to send email, because SMTP does not itself include any authentication mechanisms.
IMPORTANT NOTE: This relates to mail sent FROM your domain, not incoming emails that you receive from other domains. If other people have not properly setup email authentication for their own domain, they will also have the same issue. In order to protect yourself from malicious incoming emails from other people, you need email filtering.
What is DMARC?
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) is an email authentication protocol. A DMARC analyzer is intended to give email domain owners the ability to protect their domain from unauthorized use, known as email spoofing.
DMARC analyzer allows a domain owner to publish a policy in their DNS records that specifies which mechanisms are used to authenticate email messages sent from their domain, and what to do if authentication fails. The DMARC tool builds on top of 2 other email authentication protocols: SPF and DKIM.
DMARC has three basic purposes:
- To verify that the sender’s email message is protected by both DKIM and SPF protocols.
- To inform the receiving mail server what it should do if neither of those email security protocols passes.
- To provide a way for the receiver server to report to the sender about the email message or messages that fail or pass the DMARC evaluation.
Did You Know
468,000 Global emails were attacked
in March 2020 alone
SPF, DKIM, DMARC explained
Cyberattacks using email as an entry point have become more creatively sophisticated and technical over the years. Even during the pandemic, cyber-criminals have taken advantage of the uncertainty.
Understanding SPF, DKIM, & DMARC
SPF, DKIM, and DMARC are the three main email security protocols that complement one another.
They are methods to authenticate a mail server and help prove to Internet Service Providers (ISPs), mail services, and other mail servers that senders are truly authorized to send an email.
What’s the Importance of SPF, DKIM, DMARC?
-
 Enhances your email security posture
Enhances your email security posture -
 Combat phishing & spoofing as you're verifying the IP address of the sender.
Combat phishing & spoofing as you're verifying the IP address of the sender. -
 Keeps your domain off the global blacklists.
Keeps your domain off the global blacklists. -
 Improves domain reputation.
Improves domain reputation. -
 Improves the overall deliverability of your emails.
Improves the overall deliverability of your emails.
SPF: Sender Policy Framework
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) works by strictly determining the number of allowed IP addresses that can send emails from your domain. The idea behind the use of SPF is that if the recipient knows who sent the email, they are more likely to open it.
SPF has three major elements
-
 The policy framework as the name implies
The policy framework as the name implies -
 The authentication method
The authentication method -
 The specialized headers in the email itself that conveys the data
The specialized headers in the email itself that conveys the data
DKIM: Domain Keys Identified Mail
DKIM authentication ensures that the content of the email is trusted and has not been compromised or tampered with during the delivery.
If SPF is like the return address of a postcard or letter, DKIM is likened to sending that postcard or letter through special or recorded delivery that further builds trust between the receiver and the sender server.
At the most basic level, DKIM works by adding a digital signature to the email message header.
- DKIM also uses an encryption algorithm that creates electronic keys - a private key and a public key.
DMARC Has Three Basic Purposes
To verify that the sender’s email message is protected by both DKIM and SPF protocols
To inform the receiving mail server
what it should do if neither of those email security protocols passes.
To provide a way for the receiving server to report to the sender
about the email message or messages
that fail or pass the DMARC evaluation.
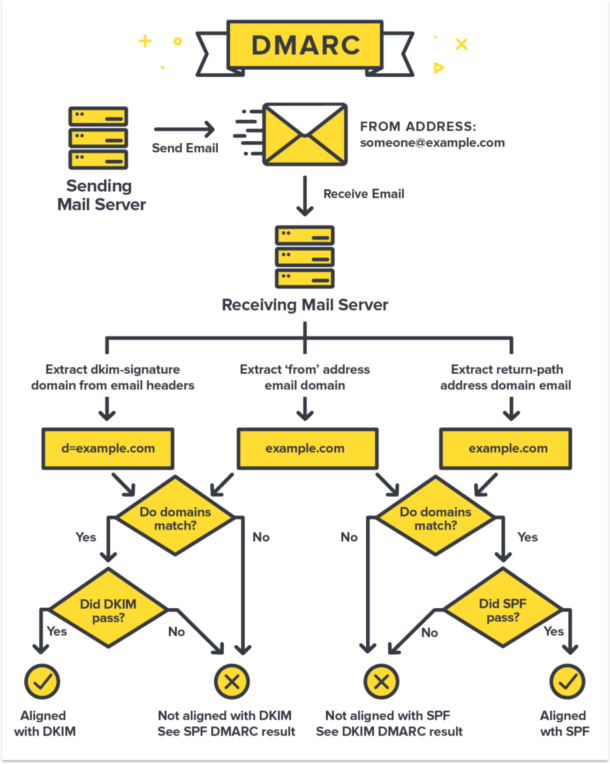
What DMARC Does
DMARC lets you tell ISPs how you want them to behave if SPF and DKIM fail or are not present. Here’s a diagram showing how SPF and DKIM work together with your DMARC policy.
Similar to SPF and DKIM, this policy resides in DNS. A typical DMARC record in DNS will look like this:
_dmarc.domain.com TXT v=DMARC1\; p=reject\; pct=100\; rua=mailto:[email protected]\;The record above sets a policy to reject (p=reject) 100% (pct=100) if the email do not pass DKIM or SPF. Additionally, you can have ISPs send aggregate reports about these decisions to an email address (rua=mailto:[email protected]). There is also a lot more to this record and policy that we won’t go into here.
ISPs who support DMARC will then generate reports on sending activity for your domain. The reports are XML files that are emailed to the email address specified in your DMARC record. The reports contain the sending source (domain/IP) along with whether the message passed or failed SPF and DKIM.
This is one of the best aspects of DMARC. Not only does it allow you to control email security for your domain, it also gives you deep visibility into who is sending on your behalf AND if they are signing with DKIM or passing SPF.
But processing these reports manually would be nigh on impossible, as you could receive hundreds per day, and these XML reports are not readable to the average layman.
This is where managed DMARC services come in, they receive and process these XML files for you automatically and generate simple, easy-to-read aggregate reports.
Order Services
Choose your desired service below.
Please note that if you go for the implementation only option and plan to do the ongoing management and monitoring yourself, then we recommend to use EasyDmarc for this..
Implementation/Setup covers alignment for up to 3 email sources (e.g. gmail, website, CRM, mailing list etc) and then 2 weeks of monitoring for issues, if you have more than 3 please get in touch for a custom quote.
Requirements:
Access to your current email provider and all other services that are used to send email from your domain.
Access to your DNS records/provider.
Implementation Only
Initial setup, you take care of the Dmarc management & monitoring yourself- Setup SPF Authentication
- Setup DKIM authentication
- Setup Dmarc Record
- Verify Alignment
- Perform Email Investigations
- Up to 3 email sources
- Dmarc Monitoring
- Blacklist Monitoring
- Fix Dmarc Issues
- Monthly Management
Power DMARC Basic
Implementation with monthly Management/Support. £150 setup- Setup SPF Authentication
- Setup DKIM authentication
- Setup Dmarc Record
- Verify Alignment
- Perform Email Investigations
- Dmarc Monitoring
- Blacklist Monitoring
- Fix Dmarc Issues
- Monthly Management
- Detailed Aggregate Reports
- Forensics Viewer
- Aggregate Geomaps
- Threat Map
- Power Analyser
- Mail Analyser
- Hosted MTA-STS
- TLS Reporting
- Hosted BIMI
- Subdomain Detection
- 2 Factor Authentication
- Basic PDF Reports
- Power SPF (SPF Flattenning)
- CSV Aggregate Reports
Power DMARC Plus
Implementation with monthly Management/Support. £150 setup- Setup SPF Authentication
- Setup DKIM authentication
- Setup Dmarc Record
- Verify Alignment
- Perform Email Investigations
- Dmarc Monitoring
- Blacklist Monitoring
- Fix Dmarc Issues
- Monthly Management
- Detailed Aggregate Reports
- Forensics Viewer
- Aggregate Geomaps
- Threat Map
- Power Analyser
- Mail Analyser
- Hosted MTA-STS
- TLS Reporting
- Hosted BIMI
- Subdomain Detection
- 2 Factor Authentication
- Basic PDF Reports
- Power SPF (SPF Flattenning)
- CSV Aggregate Reports
Implementation Services Scope (per domain)
Initial setup and validation of the following DNS records for each domain.
- EDMARC
- EDKIM
- ESPF
- EMTA-STS
- ETLS-RPT
- EBIMI (additional charges if required)
One time alignment and configuration of the identified legitimate 3rd party email sending sources
- EIdentifying and confirming legitimate email sending sources
- EConfiguring and aligning SPF and DKIM for the confirmed legitimate sending sources
- EEnsuring DMARC compliance of all emails originating from legitimate sending sources
- EIdentifying illegitimate and unauthorized email sending sources
SPF Record Optimisation.
- EError fixing
- ERemoving unnecessary lookups
- ERemoving recursive lookups and SPF loops
- EOptimizing the number of lookups using PowerSPF
DMARC enforcement
- EMoving the domain’s DMARC policy from p=none to p=reject
- EPublishing, hosting and fully managing a BIMI logo for each DMARC enforced domain via PowerBIMI (if applicible)
MTA-STS and TLS-RPT implementation
- EGenerating and publishing an MTA-STS policy file for each domain on testing mode via PowerMTA-STS
- EInvestigating, troubleshooting TLS encryption and inbound deliverability issues observed for emails addressed to each domain
- ERecommending actions to resolve the observed TLS encryption and inbound deliverability issues observed
- EEnforcing TLS-encryption of inbound emails by updating MTA-STS mode from testing to enforce

