This is a topic I have found myself explaining a lot over the years, not just to customers but to developers as well, and one thing I can say with absolutely certainly from dealing with hundreds of developers of all levels over the years, from newbs to gurus, is that most devs in general do not really understand how things work on the server (they know how to write code and upload it to the server) and most CF devs additionally don’t understand how ColdFusion really works and how/why it differs from other scripting languages like PHP or Perl or ASP.net, so I decided it was time to write a complete blog post on the subject and hopefully to try and enlighten some of those developers a bit more. I have copied this article across from my old blog as it was a popular article with a lot of views. I have removed all references to Railo (since it is now dead) and replaced with Lucee.
Now I have heard many say “I am just a developer, it is my job to write code, not to understand the server stuff”, but i’m afraid I disagree with this and consider it a bit of a cop out, because If you don’t understand how things work on the server to at least some degree, how can you be sure you are writing code that is going to be scalable, reliable and is not going to cause problems? Sure no-one should expect you to know EVERYTHING to the same level as a sysadmin, but you certainly should know the basics that are relevant to your job, especially if you are going to be making any hosting recommendations to your clients, which most devs do.
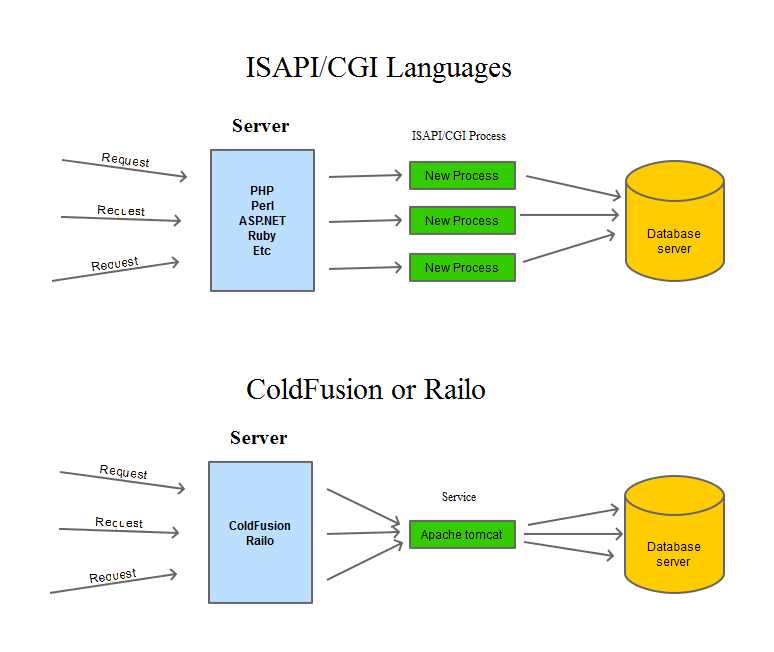
The first thing to understand, is that ColdFusion and Lucee are not technically application servers (which most people believe them to be), they are simply Java applications (that convert CFML into Java bytecode) that run inside a java servlet container (e.g. Apache tomcat, Jetty, Jboss) which runs as a service/daemon, and all requests for all pages coming into the server go through that same service/daemon. This means that any problems with that service affect ALL CFML (or JSP) websites on the server.
This is also a bad thing for security because it means that all sites on the server run within the security context of the service and so cannot have their own permissions. So any java code in any site can access files in site2, site3 or any other site on the server or in fact any part of the system that the service itself has access to. The only way round this is to use security sandboxes, which is a feature of ColdFusion enterprise and Lucee.
But BEWARE, CF sandboxes can give a false sense of security, they are only applied to CFML code and do not sandbox Java, so if you drop any Java code in your CFML pages (using CreateOnject(java), then you bypass the sandbox completely, so they not stop any vaguely competent coder/hacker. There is no way round this on a shared server, you simply have to take the risk. On a dedicated VPS you can mitigate this by using multiple instances of CF/Tomcat and isolating each site using server side permissions.
Before you say “so hosts shouldn’t allow Java”, this also is not even an option for any host as all moden frameworks and apps need createObject(java), so disabling this function would break almost every modern application, ergo it is a risk that has to be taken, because at the end of the day 99% of clients simply don’t care about the security risks, all they see is that their app doesn’t work and will just go elsewhere.
When we look at other common languages such as PHP, Perl, asp.net etc, these run as an ISAPI or CGI process, so every website on the server spawns its own process to handle the requests. So if there are 20 PHP sites then there are 20 x PHP processes running (think of this like 20 instances of ColdFusion). The process runs within the security context of the website that spawned it, so in the case of Windows it runs under the application pool identity. So this means that as long as you have every website/application pool set to run under a different user account with access only to that website root, and so will php also have only this permissions, so it is more secure and also isolates each site in a separate process.
So if site1 crashes php or ASP, it will have no effect on any other site because they are running php/ASP in a separate process.
Here is a diagram to illustrate.
This is the primary reason why CFML is not suited to shared hosting, no application isolation and no control over security.
Imagine the following (very common) scenario.
abc.com makes a cfhttp request to an external web service at xyz.com to get syndicated content for its pages.
The web service at xyz.com goes down, which means all the pages on abc.com are now going to timeout. On a shared server this will very quickly result in all the ColdFusion max number of simultaneous requests to be consumed, and subsequent requests to then become queued. The result of this is that every other CFML site on the server now becomes slow as well as all their page requests have become queued behind the problematic site, and now are likely to also timeout as a result.
An even worse scenario is where native java requests are concerned, such as database queries as these cannot be killed automatically, not even with FusionReactor. If a page hangs in the middle of a database query because it is waiting for a response back from the db server, then this request will not ever timeout and will hang indefinitely, thus 1 cf thread is now no longer available. If this happens 10 times, now 10 cf threads are gone and no longer available, if your “max number of simultaneous requests” is set to 10, then you now have 0 requests left and your server will stop serving up CFML and all websites will now hang/timeout untill the service is restarted.
If the original problem still exists then restarting CF also will not help, as the issue will simply continue until all the requests are again used up and all sites start to hang. The only solution at this point is to turn off the site causing the problem.
Then we have the security issues that I mentioned. Everyone by now is aware of the CFIDE hack which affected many cf servers. This was only possible because CF runs as service and because that service runs under the SYSTEM account by default, which has full file system access, which allowed the uploaded hack to access every part of the server. If CF worked like a CGI/ISAPI application, the effect of this hack would have been far less.
But my code has proper error trapping and caching and stuff, so this doesn’t affect me right ?
Wrong i’m afraid, on a shared server it doesn’t matter how brilliant your code is, or how well your have performance tested it, or how much error trapping you have, this does not stop the other sites on the server from causing you problems.
You could be lucky on a shared host for months or even years if you are on a server that doesn’t have many sites, or simple sites that are not problematic (at the moment), but It only takes one poorly written app to bring CF to its knees.
It is also important to realize that almost nobody using shared hosting has ever done any kind of load testing or performance testing on their website and in most cases do not even know what this means or how to do it, the result of this is that web site owners have no idea how their site will perform under load nor did the developer who made it. This results in another very common scenario which usually begins with a statement like “Nothing has changed on my site and it has been running fine for years, so it must be your server”.
Again this is totally irrelevant in most cases, sure your site may well have run fine for years with 20-50 visitors per day, but what happens when it suddenly gets 1000 visitors per day as a result of some marketing or media attention, or if it starts getting hit by search engine bots, suddenly this once stable site falls over horribly due to poorly written or legacy code.
But Railo/Lucee is better right ?
Ultimately no i’m afraid, as they run on Java so work the same way as CF so the primary issues mentioned above apply just the same.
Lucee is however an improvement in that the security sandboxing is automatically applied at website context root level (if you set this in your Lucee server admin) and does not require admins to set up sandboxes for each site as with ColdFusion which is a sandboxing nightmare, which makes Lucee better for shared hosting. However the sandboxes like ColdFusion’s only sandbox CFML and can easily be overridden with Java code.
Lucee also has its per site web admin allowing all users to admin their own site, which is again a bit improvement over ColdFusion which has a single Admin which must be administered by the host.
So by using Lucee you don’t have to rely on your host, you can pretty much do everything yourself.
So what’s the solution ?
The only solution is to do some research, educate yourself and use a bit of common sense.
ColdFusion is intended to be an enterprise solution, and thus run on dedicated hosting solutions, it was never intended to be used for shared hosting and is not built to do this. So the simple answer is, use the right tool for the job.
If you just want to run a blog, personal website or simple brochure ware website and you don’t have your own server and only have the budget for shared hosting but do not want to be affected by the above problems, then use a technology more suited to this purpose, one that runs as a CGI/ISAPI process, the most popular of course being PHP or ASP.net . Avoid any Java related choices as these will all suffer from the same issues.
If you love CFML and want to use it for everything you do, then do yourself a favour and get a VPS running Lucee (or ColdFusion if you can afford it).
On your own VPS you then also have the option to use multiple CF instances, so each of your sites runs on a dedicated instance of Tomcat or whatever is your java servlet container of choice, so you can still run multiple sites but avoid the shared hosting scenario and also lock down the security.
I am going to use shared hosting anyway regardless, what do you suggest ?
If you really have no choice (or simply won’t take good advice), then here are some tips on choosing a host.
- Choose a host that specializes in Lucee or ColdFusion and actually knows what they are doing, do not choose a generic host that simply has Lucee/CF installed and classes this as SUPPORTED.
- Test your hosts knowledge, see how much they know about CF/Lucee, ask to speak to a CF specialist.
- Make sure your host is secure
- For ColdFusion they should be using enterprise edition, otherwise no sandboxes, and no security. If they are running standard edition, avoid.
- Ask them if they run a bog standard out of the box CF installation, if yes then it is not locked down and is not secure.
- Ask them if they use FusionReactor or HackMyCF. Preferably go with someone who says yes.
- Ask them if they use security sandboxes, if no then avoid.
- Ask your host how many sites they run on each CF server. Too many = bad
- If you regularly need to set up data sources, mappings or anything that requires access to the CF Admin, you would be better of with Lucee.
- Ask if you can get RDS access, if they say yes then avoid, as this should not be enabled in production
- Check if you can access the cfadmin or adminapi from your site, is yes, change host now as they are not secure.
Unfortunately there are very few noteworthy CF hosts these days, the ones I see most commonly recommended are Viviotech, Hostek, HostMySite (although not so much since they got taken over by hosting.com), Host Partners (my company)