Email is a leading communication tool for businesses around the world. It’s widely used for both internal and external collaboration. Nevertheless, it’s not innately secure, and is email spoofing is commonly used by cybercriminals.
Email spoofing is the creation of email messages with a forged sender address. Criminals will use this technique to send emails purporting to be from YOUR domain.

Cybercriminals actively use email channels to distribute malware, spread viruses, and trick users. According to research by PurpleSec, 66% of malware is installed via malicious email attachments.
On its own, even the best secure email for a small business or mega corporation isn’t enough. Whether an organization is large or small, it still needs to integrate business email security best practices. Another study shows that 43% of cyber attacks target small businesses. Hence, hackers threaten businesses regardless of size and type.
Read on to discover 10 email security best practices for business owners in 2022. You’ll learn how to prevent possible attacks and bypass data vulnerability.
What Are The Best Practices for Business Email Security for 2022?
Although there are numerous strategies to get you the most secure business email, they’re always evolving and bringing new trends.
With the following business email security best practices, you can get measurable results—but only with a strategic, consistent, and permanent approach.
#1: Implement Email Authentication Protocols & Domain Alignment
Email authentication protocols (DMARC, DKIM, and SPF) are used to authenticate messages sent from your domain. They help prevent phishing, email spoofing, and other cyberthreats. In simple terms, the sending and receiving mail servers talk to each other and double-check authenticity in the DNS.
Besides security, enhanced brand trust and improved deliverability rates are major advantages of email authentication protocols.
What is DMARC Alignment and Why Is it Important?
Alignment is a key concept in the introduction of DMARC; it is the requirement that the domain used for either a passing SPF or DKIM result MUST match the domain of the From header in the email message body.
Though SPF and DKIM are mostly familiar technologies, it’s important to understand that neither SPF or DKIM, on their own, have anything to do with the From address, which is what humans typically see on an email. This is why phishing, spoofing, Shadow IT and other unchecked/misuse of domains run rampant today. There are very few controls that prohibit bad actors from sending an email as you. The primary control to observe and restrict email domain usage is DMARC.
If you need help with setting this up, get in touch.
#2: Use Two-Factor or Multi-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication is a crucial feature of secure business email. Hackers often steal passwords and login credentials to carry out their attacks. But if everybody in your organization has two- or multi-factor authentication, login details alone aren’t enough for hackers to achieve their goals.
To gain access, cybercriminals need another code usually sent to you via SMS, a voice call, an email, or a one-time password from an authentication app. If you haven’t already, implement two- or multi-factor authentication to defend against common email security issues for the most secure business email possible.
#3: Detect and Prevent Phishing Emails
Phishing emails are often tricky to identify. Cybercriminals use impersonation tactics to make the message appear legitimate and as convincing as possible. That’s why companies must pay special attention to increasing phishing awareness among their employees.
Phishing emails are typically disguised as official emails from legitimate service providers. They’re designed to trick recipients into taking certain actions like divulging confidential data, revealing login credentials, or clicking on malicious links.
Cybercriminals use reasons like suspicious login activity on your account, problems with payment settings, new documents, or available updates to execute their phishing scams. But if you’re cautious enough, you’ll notice mistakes in the email address and grammar of the text that makes the message doubtful.
It is also important to note that the email provided by most ISP’s or hosting providers is very basic and has very little security. I recommend using a more robust business email solution such as Google Workspace or implementing an email scanning/filtering solution. I do offer both of these as a managed solution.
Is Gmail Secure against Phishing?
Hackers use “phishing“ attacks to either steal your data or get control of your computer. They’ll send you an email with either a link or an attachment. If you open it, they’ll have access to your computer.
In our tests, Gmail is much better than Microsoft365 or Yahoo Mail at stopping spam and phishing emails. While Microsoft365 has announced some better spam and phishing detection, we’ve been very happy with the long term performance of Gmail.
Google built “the first computer program to ever beat a professional player at the game of Go.” These “machine learning” programs are also great at spotting bad emails.
When it comes to spotting phishing, we think Gmail is the best game in town.
Is Gmail Secure against Sniffing?
Hackers can listen in on your web traffic. You’re especially vulnerable if you’re using wifi in a public place like McDonalds or a coffee shop.
In 2014, Gmail started forcing all traffic to use HTTPS. This stops hackers from listening in on your email on insecure wifi networks.
You can tell if you’re using HTTPS by looking at this lock in the address bar of your browser:
HTTPS on:

HTTPS off:

Is Gmail Secure against Password Guessing?
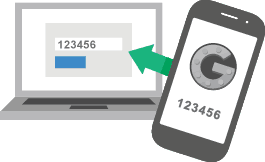
Another way that attackers can use to get into your account is to try to guess your password. Gmail keeps you safe from these attacks in three ways:
a) 2 Factor Authentication. We HIGHLY recommend you use this. When it’s turned on, you’ll need to use an app or a text message on your phone to get into your account.
Gmail has done a better job of 2 Factor Authentication than other companies. It’s easy to use. It also only asks for your code if you’re doing something weird (like logging on from a new computer).
If you don’t have access to your app, it also lets you get codes via text message…
And they’ll give you some backup codes you can use if you don’t have your phone handy…
b) Password guessing. If someone tries to log in to your account over and over, Google will lock them out. People call this a “brute force attack.”
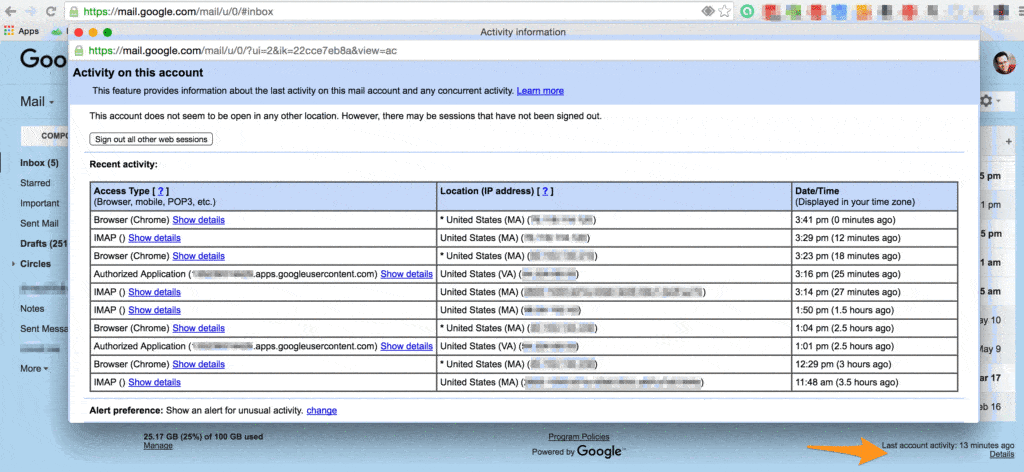
c) Activity on this account. We love this — with the click of a button, it’s super easy to see exactly where your account is being used. You can also click a button to lock out other sessions.
#4: Be Careful When Using Public Wi-Fi
Any actions you take using public Wi-Fi can be easily monitored by hackers. Using open-source packet sniffers is enough for them to access your information. Even if you’re connected to public Wi-Fi but haven’t logged into your corporate email, your information is still automatically updated. And this is how you put your account credentials at risk.
Any connections you use over a public wifi should always be encrypted with SSL (HTTPS). If you are unsure, don’t use it.
#5: Train Your Staff on Email Security
In an organization, its problems are directly related to all employees․ Training your staff on good business email security practices and why they’re important is crucial in today’s digital age.
Consider implementing phishing awareness and email security protocols to keep your team informed on current threats and modern corporate security policies. Email phishing tactics keep evolving; so it’s essential to stay up to date on new security measures.
#6: Choose Strong Passwords
Once there was a stereotype that a complex password must be as long as possible, but this is no longer the case. If you want to be able to easily remember and type the password, then it is recommended to make up a phrase, such as “skinny jeans make my bum look fat” or 4 or more random words, for example, “Pencil Uniform Obliterate Arsenal”.
Still, if it’s easy to crack it will be cracked, no matter the number of characters. so don’t use common/known phrases, such as “live long and prosper” all the names of your kids or characters from a TV show, e.g. “George bungle zippy Fred”.
But remembering lots of passwords is hard no matter what you do. So If you are not currently using a password manager, then I highly recommend doing so. This is the best way to generate and manage your passwords without having to remember them.
Read my article “Why you should be using a password manager”.
#7: Never Use Corporate Email For Personal Use
Sending personal messages from a corporate email adds to the risk of phishing attacks. To enhance email security best practices for business, avoid using a corporate email outside the scope of its functions. The same applies to personal email accounts. Work-related emails must always be sent from the organizational domain.
Before launching any phishing attack, cybercriminals harvest information online using special tools. A target using a corporate email for personal purposes is vulnerable in the eye of an attacker. It’s easier to implement an attack and spread malware.
#8: Never Click on Links or Download Attachments in a Suspicious Email
Business email security best practices include dealing with suspicious messages. Often, the link in a cyberattack email displays a recognizable domain name but directs the user to a malicious source. Use the latest antivirus or anti-malware tools to avoid malware installation upon clicking.
Attachments and links are the primary sources of malicious content. If you hover over the actual link and see a different display link, never click on it. Rather check the link by typing it in a new window.
Using a good email security solution that blocks known phishing emails and websites will help to avoid this.
#9: Regularly Update Your Privacy Settings
Cybercriminals are always cultivating new scam methods. That’s why businesses must regularly update their privacy settings to detect breaches or suspicious activities. If you notice an unauthorized login attempt to your account, consider taking steps to amplify your business email security.
#10: Don’t Send Business Emails From Unsecured Devices
While outside the office, employees may use personal devices to log into their corporate accounts and send emails. This practice became increasingly common as remote working spiked amidst the COVID-19 pandemic. But a personal computer or another non-work device may lack protection and become easily infected with malware.
Use your corporate account on work-safe devices and implement advanced email security software. This helps prevent email phishing threats, impersonation, and other malicious cyberattacks.
Final Thoughts
Security enhancements are vital for all business email accounts But they’re not enough on their own. Email security best practices for business are equally as crucial. Implementing these measures helps protect your company and your network from cyber threats.
Cybercriminals are quite skilled at manipulating people. That’s why identifying their tactics and implementing cybersecurity policies is a must for all organizations and their staff.
Need Help ?
If you need help in implementing any of these suggestions, feel free to get in touch, I provide various managed security services including- Google Workspace, Bitdefender gravity zone, email security, domain alignment, dmarc monitoring and reporting and more.
checkout my Managed Dmarc service.







